1. Detection
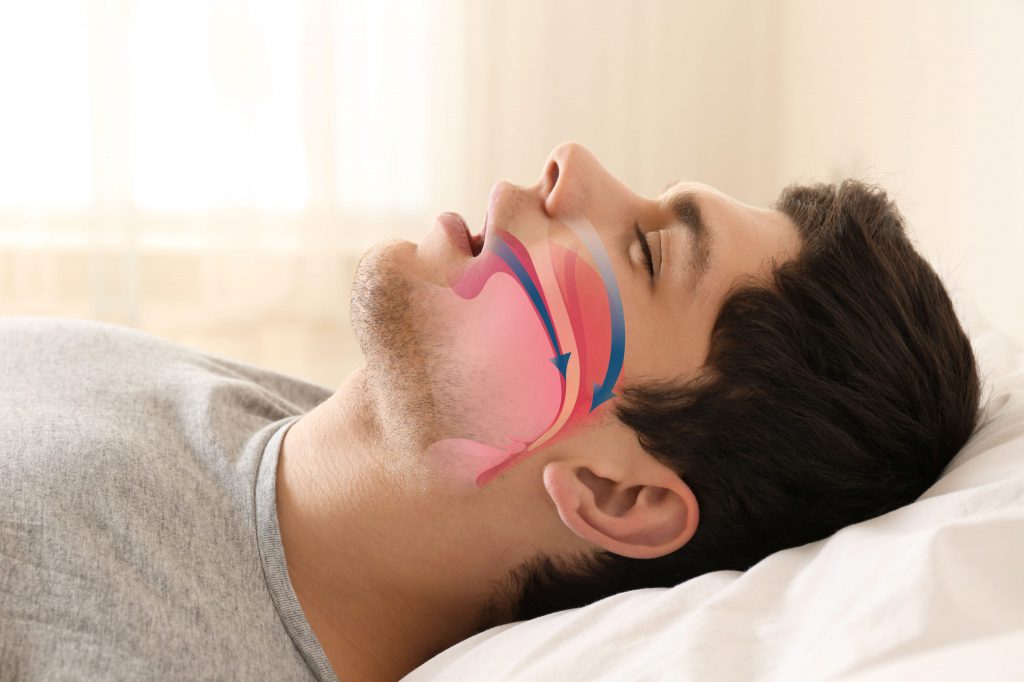
The detection of OSA begins with the evaluation of the patient’s symptoms.
Some common signs include persistent loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, breathing pauses during sleep, and frequent awakenings during the night. It is important that the patient or those close to the patient report these symptoms to the doctor for proper evaluation.
2. Diagnostic
Accurate diagnosis of OSA is made by sleep studies, which are prescribed by a doctor specializing in sleep disorders, such as a pulmonologist, neurologist or sleep medicine specialist.
The most common study is polysomnography, a study in which several functions are monitored during sleep, such as brain activity, eye movement, muscle activity and breathing.
Home sleep monitoring can also be used in selected cases. These studies provide objective data on respiratory events during the night, allowing accurate confirmation of the presence and severity of OSA.
3. Treatment
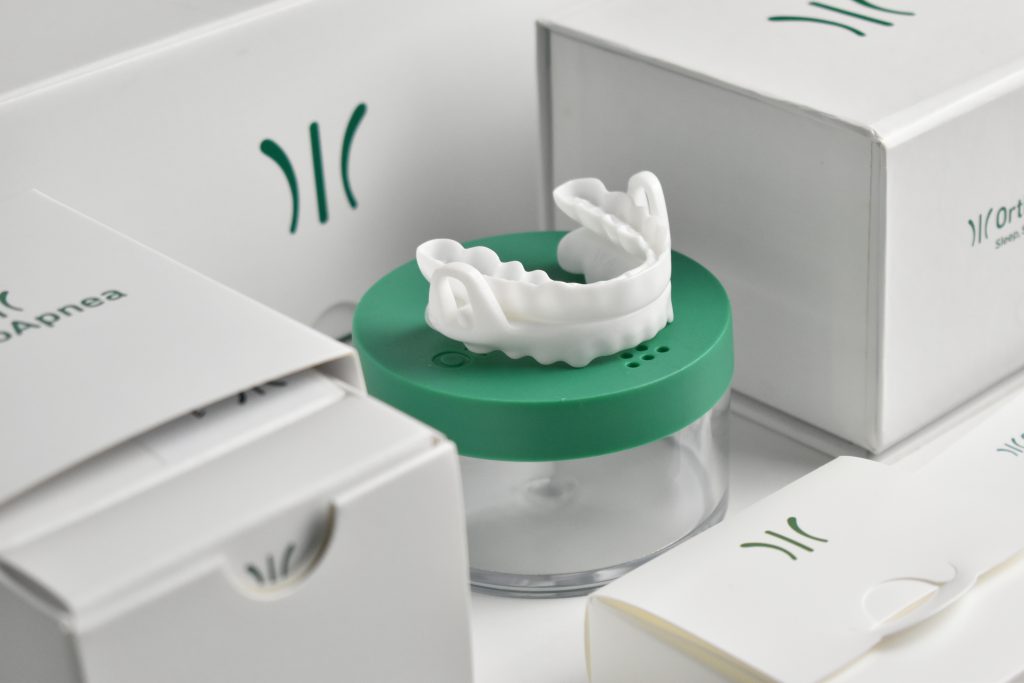
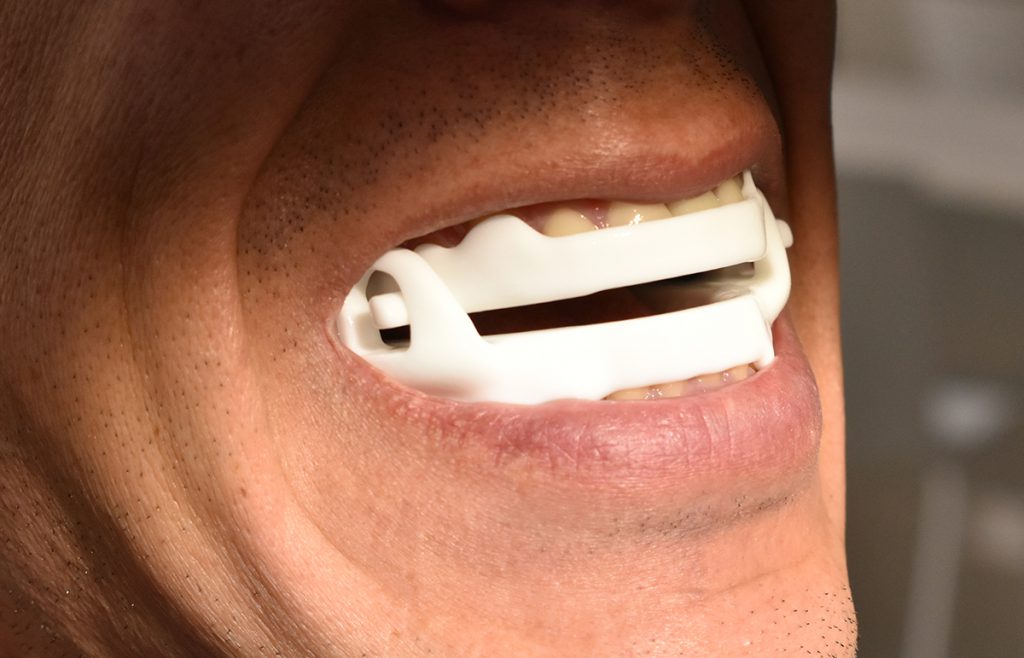
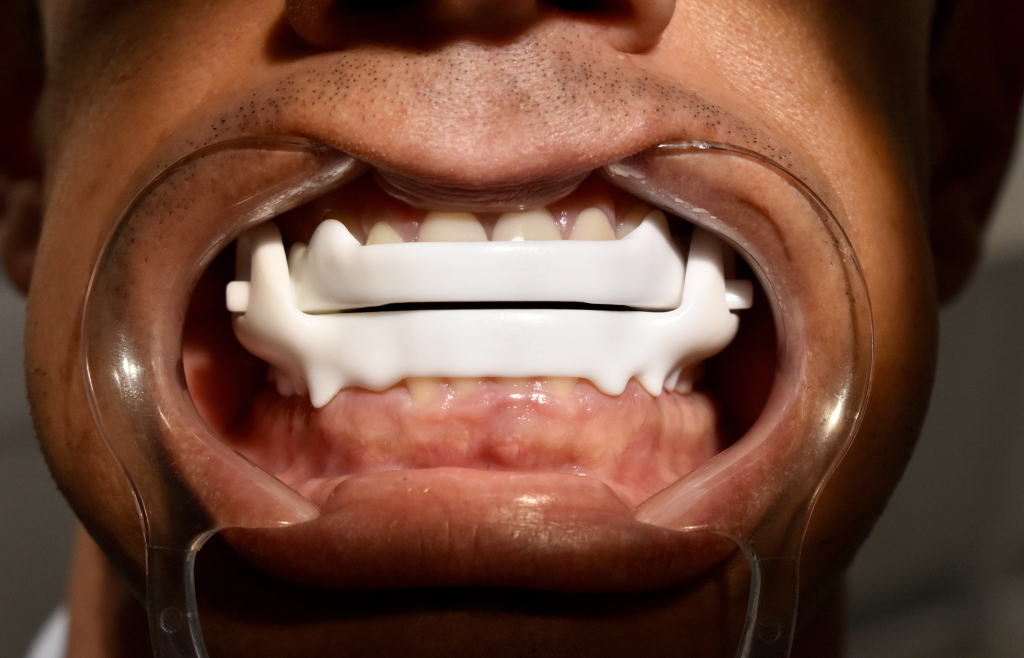
Once the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is confirmed, one of the most common and effective treatments is the use of the Mandibular Advancement Device (MAD). This medical device is prescribed by a dentist specialized in sleep disorders.
MAD offers several benefits for patients with OSA. It is comfortable to wear and easily adjustable to suit individual needs. It is also a non-invasive alternative to other treatments, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP).
Some patients find MAD more tolerable and can use it consistently and effectively.
4. Follow up
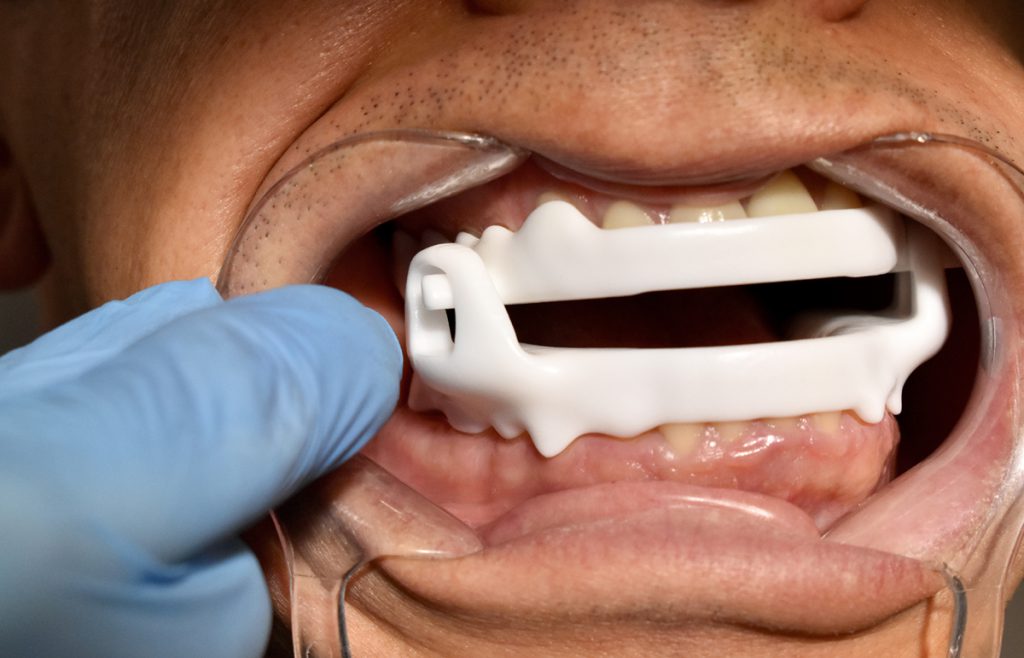
The regular follow-up of the patient is performed jointly by the dentist and the sleep unit.
These professionals work collaboratively to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment with the Mandibular Advancement Device (MAD) and make any necessary adjustments. During follow-up visits, the patient’s response to the MAD is evaluated, the correct adjustment is checked and modifications are made if necessary. In addition, both the dentist and the sleep unit can offer additional recommendations to improve sleep quality and ensure proper adherence to treatment.
This multidisciplinary approach ensures effective management of OSA and comprehensive patient care throughout the treatment process.